The conclusion of 2025 became not just another stage in the evolution of search algorithms, but a true turning point for the entire SEO industry. What previously seemed like gradual development turned out to be a fundamental transformation of the very nature of search. While we used to talk about the shift to mobile indexing or the implementation of semantic analysis, 2025 was marked by the final transition from link-oriented search to an agentic environment driven by artificial intelligence.
The central element of this transformation was the implementation of the MUVERA architecture, which allowed Google to overcome the limitations of single-vector data compression models. Technically, this ensured 90% faster information processing with a 10% increase in accuracy compared to the previous year’s models. But the real revolution took place not in technical specifications, but in the very approach to providing information to users.
Chronology of Algorithmic Updates in 2025
Over the past year, Google released three massive Core Updates and one powerful Spam Update, each of which had a specific impact on different segments of the web space.
March 2025 Core Update: The First Swallow of Change
The March update, which ran from March 13 to 27, set a new standard for content quality. The main focus was on prioritizing unique perspectives and combating superficial AI content. This update was the first serious signal that the era of mass content generation using artificial intelligence without human oversight was coming to an end.
Sites that used a template approach to creating materials suffered the most. Medical blogs without proper expert review, affiliate resources with lists of "best products" without real testing, and general advice without practical examples lost a significant portion of their search visibility.
June 2025 Core Update: The Most Destructive Update
The June update, which began on June 30 and ended on July 17, went down in history as Google's most destructive update. Unlike previous updates that simply redistributed positions in the SERP, the June update actively removed pages from the index.
Experts estimate that between 15% and 20% of pages were deindexed from Google's general index. Some sites lost 70% to 90% of their traffic in just a few days. The main reasons were thin content, lack of clear authorship, low value to the user, and mass use of AI without proper editing.
Interestingly, it was during this update that John Mueller, a Search Advocate at Google, reminded the community of the long-term nature of such changes. He emphasized that core updates are built on long-term data, so quick technical fixes rarely help to recover instantly.
August 2025 Spam Update: The Fight Against Parasite SEO
The August update, which ran from August 26 to September 22, was the longest spam update of the year. The main goal was to combat so-called "parasite SEO" and domain reputation abuse. This is a phenomenon where specialists paid authoritative publications like Forbes, the Wall Street Journal, or CNN to host low-quality content on their domains to take advantage of the high ranking of these resources.
Sites with high Domain Authority and strong brand signals survived this update best. Conversely, resources with an excessive amount of advertising (more than 25% ad-to-content ratio) suffered the most.
December 2025 Core Update: Reassessment of Competence
The December update, which began on December 11 and ended on December 29, was the longest of the year (18 days). It was an update of "competence reassessment" that targeted sites writing for algorithms rather than users.
Between 40% and 60% of all sites experienced measurable rank changes. E-commerce resources suffered in 52% of cases, medical and YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) sites in 67%, and affiliate sites in a whopping 71%. An interesting feature of this update was that some winners of November received penalties in December, indicating further tuning of the algorithm.
"Core Updates are based on long-term data."
John Mueller
Evolution of E-E-A-T: From Theory to Practice
The concept of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) has existed for several years, but 2025 was the period when it turned from a recommendation into a mandatory requirement.
Experience: Real Experience as a Key Factor
The first "E" in the acronym stands for Experience, and this component became the most critical last year. It is no longer enough to simply write an article about fitness; you need to show photos of your own results. A restaurant critic must demonstrate pictures of ordered dishes. A technical reviewer must provide evidence of hands-on product testing. A lawyer must cite cases they have personally worked on.
This approach has radically changed the requirements for content marketing. Companies can no longer simply hire copywriters to write articles on any topic. Now, real experts are needed who can confirm their experience with concrete evidence.

Expertise: Demonstration of Specialized Knowledge
Expertise implies the possession of specialized knowledge in a certain field. The June update particularly tightened the requirements for this component. Google now looks for clear author credentials with links to LinkedIn or professional profiles, citations of reliable sources, and detailed explanations that go beyond superficial information.
Medical, financial, and legal sites felt this most acutely. Whereas previously one could write a general article about disease symptoms, now an article written or reviewed by a certified doctor, with references to scientific studies and clear disclaimers, is required.

Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness: Trust as Currency
Authoritativeness means recognition of position in the industry through awards, certifications, mentions in authoritative publications, backlinks from relevant sites, and consistent publishing on the topic. Trustworthiness includes transparent contact information, SSL certificates, clear privacy policies, absence of manipulative tactics, and quick content updates when new facts appear.
Danny Sullivan, Google Search Liaison, highlighted the critical role of brand in modern SEO. According to him, brand recognition is an important correlate of success not because the company is a brand, but because people recognize it. In a world where content can be generated instantly, trust in the source becomes the main ranking factor.
The Zero-Click Crisis: The New Reality of Search
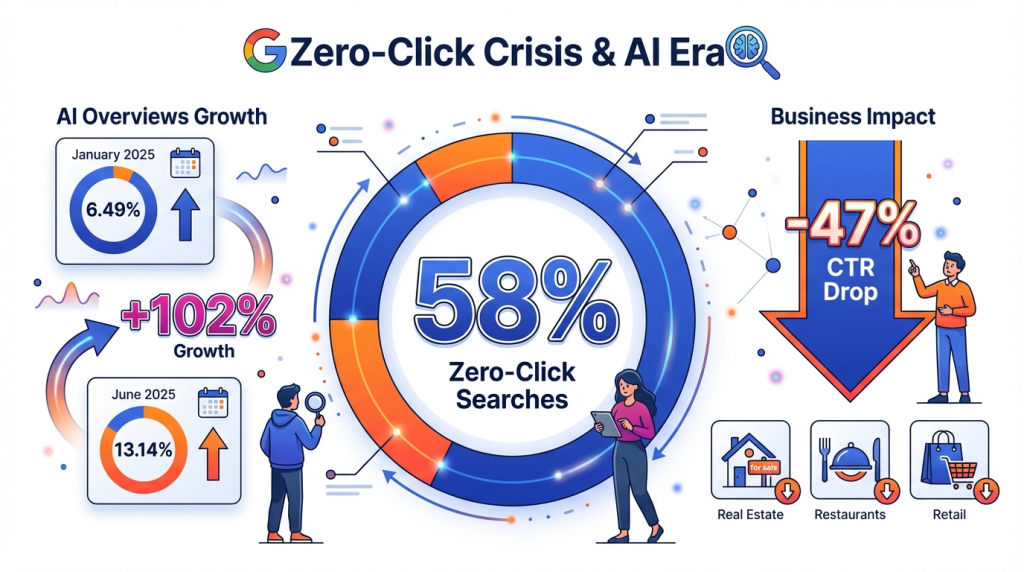
One of the most alarming trends of 2025 was the zero-click crisis. Data for November showed that 58% of Google search queries end without clicking through to a site. This means that more than half of all searches generate no traffic for web resource owners.
AI Overviews: A Double-Edged Sword
The main driver of this trend became AI Overviews, previously known as SGE (Search Generative Experience). When Google launched this feature in May 2024, many hoped it would be a limited phenomenon. Instead, in 2025, AI Overviews became the dominant factor in the organic traffic crisis.
The statistics on the spread of AI Overviews throughout the year look impressive. In January 2025, they appeared in only 6.49% of queries. By March, this figure rose to 8-10%, representing moderate growth. In June, the share reached 13.14%, which was over 102% growth in five months. Experts forecast that by November, this figure reached 15-20%.
Informational queries suffered the most, with AI Overviews appearing in 88.1% of cases. Navigational queries also began receiving AI responses, though more slowly. Commercial queries expanded the slowest, but the trend was obvious.
Impact on Click-Through Rate
Seer Interactive research showed a dramatic drop in CTR (Click-Through Rate). If the average CTR without an AI Overview was around 15%, with the appearance of an AI response, it fell to 8%, representing a 47% decrease. Separate studies recorded even more dramatic figures: a drop from 1.76% to 0.61%, i.e., by 61%.
Pew Research Centre research found that 26% of users end their search session immediately after viewing an AI Overview, without navigating to any site at all. This creates a paradoxical situation: users get answers to their questions, but content creators receive no reward for their work.
Categories at Highest Risk
SparkToro research identified categories with the highest risk level. Real estate saw a 258% increase in AI Override appearance. Restaurants showed 273% growth. Retail recorded a 206% increase. Local services also found themselves in a zone of high vulnerability.
Despite community concerns, Google’s official position remains restrained. At the Search Central Live conference, Gary Illyes, one of Google’s leading representatives, made a statement that went viral among specialists. He claimed that to appear in AI Overviews, it is sufficient to use standard SEO methods, and no special techniques like GEO or LLMO are needed.
This statement sparked lively discussions, as many specialists already see GEO as a separate discipline. However, Illyes insists that AI functions use the same infrastructure as traditional search.
"If you have an online business that earns from referral traffic, it’s definitely worth looking at the bigger picture and prioritizing accordingly… AI isn’t going anywhere, and thinking about how your site’s value works in a world where AI is available is time well spent."
John Mueller
Generative Engine Optimization: A New Discipline
Despite Google’s statements, as of 2025, GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) has become mainstream and effectively turned into a separate branch of digital marketing. The key success factor in GEO is understanding that AI engines analyze not just keywords, but subtopics of the query, context, relationships between entities, and information structure.
John Mueller's Philosophy on the Future
John Mueller has repeatedly commented on the transition to GEO in discussions on Reddit. He advised specialists to be realistic about using AI tools and look at actual metrics: what share of the audience actually uses AI tools compared to other channels.
According to him, if you have an online business that makes money from referral traffic, it is definitely worth looking at the full picture and prioritizing accordingly. AI is not going anywhere, and thinking about how your site's value works in a world where artificial intelligence is available is worth the time spent.
Practical GEO Tactics
Search Engine Journal research showed that brands adopting the GEO framework saw 40% higher visibility in generative results. Key tactics include creating direct answer blocks of 40-60 words, placing structured data via Schema Markup, entity clarity, and question-oriented content.
Direct answer blocks should be placed at the beginning of each section and provide clear, concise information. This is exactly what AI extracts first. For example, to the question "What is LCP?", the answer should be short: "LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) is the loading time of the largest visible element on the page. Google's goal: less than 2.5 seconds."
Schema Markup has become a sort of "fuel for AI indexing." FAQPage schema for question-answer pairs, HowTo schema for instructions, Article schema for content definition, Speakable schema for voice search, LocalBusiness schema for local results—all these elements help AI systems better understand and classify content.
War on AI Slop: Cleaning the Index
The year 2025 went down in history as the year of the “great deindexing” of AI slop. Google actively fought against sites that abused automatic content generation without proper quality control.
Google’s Tough Stance
John Mueller expressed himself quite harshly regarding sites that are in a “bad state” due to low-quality AI content. According to him, such resources should rethink their purpose rather than look for technical fixes. He repeatedly warned on Twitter against using LLMs to get advice on SEO, ironically noting that search is never guaranteed and no one can guarantee traffic.
What SpamBrain Detects
SpamBrain, Google’s AI system for detecting spam, underwent significant improvement in 2025. It now recognizes mass production of thin content with no original value (Scaled Content Abuse), purchasing old domains to publish spam (Expired Domain Abuse), paid publications on authoritative sites to manipulate rankings (Site Reputation Abuse), and fully automated content streams without human oversight.
The “Crawled – not indexed” Problem
In addition to deindexing pages, Google launched a new tactic in May 2025. Millions of pages received the “Crawled – not indexed” status in Google Search Console. This is not deindexing in the classical sense, but ignoring at the indexing level.
The main reasons were thin content (one or two sentences per page), low original value, content duplication, and insufficient depth of topic coverage. The recovery strategy involves not deleting such pages, but completely rewriting them with the addition of practical examples, case studies, measurable results, and primary research.
Fragmentation of Search: The End of Google’s Monopoly
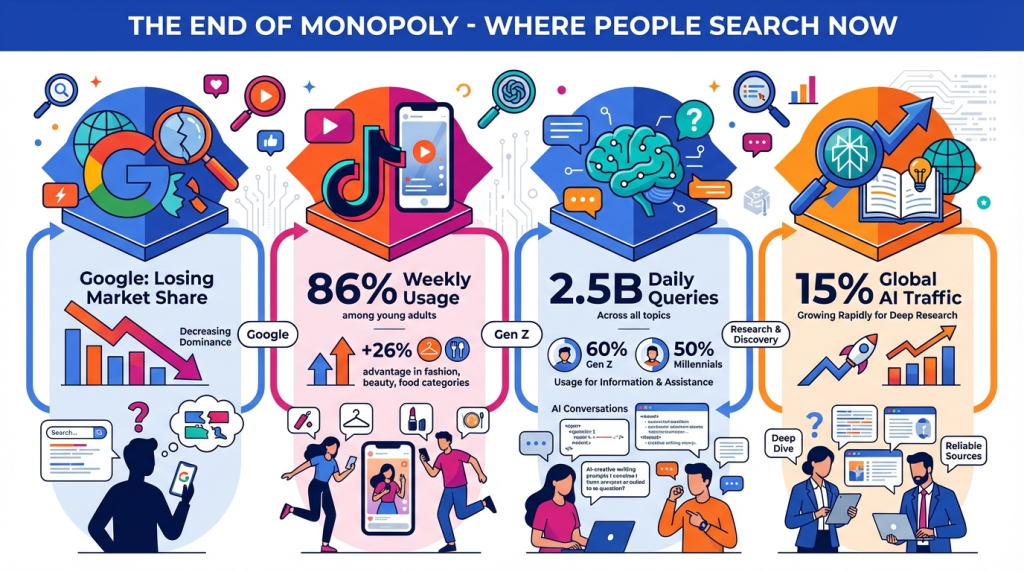
One of the biggest shifts of 2025 is the realization that Google is no longer a monopoly search engine. This happened not suddenly, but as a result of evolution over 18-24 months.
TikTok as a Search Engine
The most successful story of search fragmentation has been TikTok. Research by WARC and TikTok conducted in September 2025 showed impressive results. Generation Z uses Google weekly in 90% of cases, but TikTok is also used by 86% of this age group weekly.
But the real difference appears when looking at specific categories. For fashion and beauty, users turn to TikTok 26% more often. For cooking, the figure is 23%, for entertainment 22%, for DIY projects 15%.
The reason for TikTok's success lies in several factors. The personalized recommendation system (For You Page) works better than keywords for Generation Z. Video content is more attractive than lists of blue links. Social proof is built-in via likes, shares, and comments. Trending happens in real-time, whereas Google often lags behind trends.
ChatGPT and the Search Revolution
ChatGPT demonstrated incredible growth as an alternative search tool. In December 2024, it was predicted that ChatGPT could reach 1% market share by the end of 2025. In July 2025, Sam Altman confirmed 2.5 billion prompts per day. By November, ChatGPT had become six times larger than Perplexity.
Generation Z uses ChatGPT in 60% of cases, millennials in 50%. The practical reality is that ChatGPT as a search engine is still quite niche, but it brings significant impact in specific searches: scientific questions, programming, complex problems. For medical or financial advice, users turn to ChatGPT more often than to traditional Google search.
Perplexity: The Hidden Winner
Perplexity is talked about less than ChatGPT, but the data speaks volumes. In 2025, the service captured 15% of global AI traffic and 20% in the US. The average user dwell time on the platform is nine minutes, which significantly exceeds average indicators. Over four months in 2025, growth was 25%.
The key difference from ChatGPT is that Perplexity is a research engine, not a chatbot. Users come here to analyze trends, for academic research, and for in-depth study of issues.
"If you are recognized as a brand in your industry — big or small, it doesn’t matter — it is important. This correlates with many search success signals. Not because you are a brand, but because people recognize you."
Danny Sullivan
Technical SEO in the Era of Agentic Search
The transition to agentic search, evidenced by Project Mariner from Google DeepMind, requires new technical hygiene. Now, not only accessibility for humans is important, but also “machine readability.”
Core Web Vitals: From Recommendation to Obligation
Core Web Vitals have officially been a ranking factor since 2021, but 2025 expanded their influence. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) must be less than 2.5 seconds and is crucial for the first impression. Interaction to Next Paint (INP) must be less than 200 milliseconds and is critical for mobile devices. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) must be less than 0.1 and is often ignored, but significantly affects user experience.
The business impact of these metrics is obvious. A one-second delay leads to a 20% drop in conversions. Sites with good Core Web Vitals convert 3-5% better. 40% of users leave a site if it loads longer than three seconds.
Accessibility as a Ranking Factor
This trend emerged unexpectedly in 2025. Google has not officially announced accessibility as a ranking factor, but data clearly shows a correlation. September 2025 research found that sites with high accessibility standards saw 37% organic traffic growth.
E-commerce resources recorded 50% traffic growth and 30% sales growth. News sites saw a 40% drop in bounce rate on mobile devices and a doubling of time on page.
The link between accessibility and SEO is tight. Accessibility means clean HTML and correct semantics, which facilitates crawling. A logical structure for screen readers is also logical for search bots. Core Web Vitals often improve during work on accessibility.
The Accessibility Strengthening Act (BFSG) came into force on June 28, 2025, and the European Union requires compliance with the WCAG 2.1 AA standard. It is expected that Google will strengthen the influence of this factor in the third quarter of 2026.
Antitrust Cases and Their Impact on the Industry
USA vs. Google Case
The US vs. Google trial, which began in October 2020, reached its climax in 2025. The first verdict was delivered on August 5, 2024, when the court found Google guilty of illegal monopoly. The remedies trial took place from April 21 to May 2025, and the verdict on sanctions was announced in September 2025.
Federal Judge Amit Mehta ruled to ban exclusive contracts for search, mandated the sharing of search index data with competitors, and required access to user interaction data. Importantly, these sanctions extend to generative AI products.
The court did not support the Department of Justice’s demands to sell Chrome or Android, which was a certain victory for Google. The company is appealing the verdict, arguing that AI has changed competition, and ChatGPT along with Perplexity are fair competitors.
Practical Impact for 2026
Competitors will gain access to Google search data, which could accelerate the development of ChatGPT Search and Perplexity. Google may delay the implementation of new AI features due to regulation. Further documentation leaks are expected, which could reveal even more details about how algorithms work.
May 2024 API Documentation Leak
Although the leak occurred in May 2024, its impact on SEO thinking in 2025 was significant. 2,596 modules and 14,014 attributes from the Google Content Warehouse API were released, totaling over 2,500 pages of documentation.
Key discoveries included the existence of a Site Authority metric (from 0 to 100 points), which Google had previously denied. The NavBoost system uses data on clicks, dwell time, and pogo-sticking from Chrome and Search Console, confirming the use of behavioral signals for ranking. New content from young hosts is subject to a “sandbox,” delaying traffic until quality signals are established.
Google provided a typical response, warning against inaccurate assumptions based on out-of-context, outdated, or incomplete information. However, the SEO community took this data seriously: 62% of agencies changed their link-building strategy within 90 days, entity stacking became more valuable, and controlled link building became more popular.
The Parasite SEO Scandal and EU Reaction
One of the most interesting stories of the year concerns Google’s fight against parasite SEO and the unexpected reaction from the European Union. In November 2024, Google issued penalties to Forbes, Wall Street Journal, CNN, and Time for hosting sponsored content of dubious quality. In February 2025, the company clarified its policy regarding site reputation abuse.
However, in November 2025, the European Union opened an antitrust investigation, claiming that Google’s policy is excessive. A paradox arose: Google claims it is protecting quality from spam, the EU insists that selective placement of guest content is a legitimate business model for publishers, and the publishers themselves complain that Google first gave them money through guest posts and is now punishing them for it.
The result has been uncertainty. Google defends its policy, but the EU investigation will delay its implementation until 2026.
Strategic Roadmap for 2026
What to Stop Doing
Guaranteeing specific positions in search no longer makes sense, as rankings have become extremely volatile. Mass production of content leads to the slow death of visibility. Traditional keyword selection is losing meaning, as AI does it better. Pure link building without contextual relevance will be penalized by Google.
What to Switch to in 2026
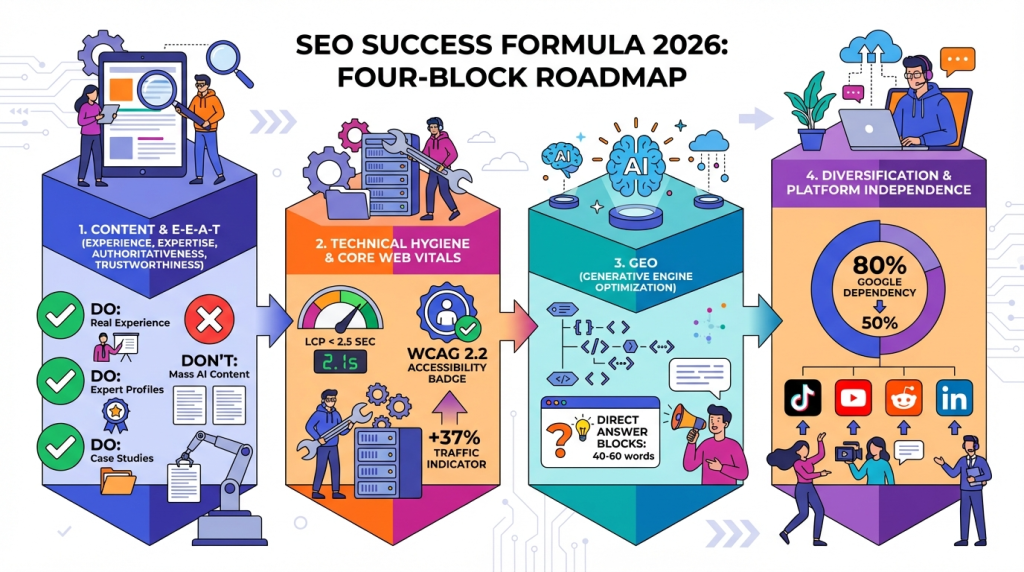
Auditing and transforming E-E-A-T must become a priority. This includes analyzing content for demonstrated expertise, adding case studies, results, photo evidence, and building author profiles with links to credentials. The result can be 15% to 40% traffic growth in 4-6 weeks for quality sites.
Answer Engine Optimization should include auditing citation possibilities in AI Overviews, updating Schema Markup (FAQPage, HowTo, Article, Entity schema), identifying the 50-100 most important questions in the niche, and restructuring content for AI compatibility. Studies show 40% higher visibility in AI results.
Generative Engine Optimization goes beyond Google AI Overviews to cover ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Each platform requires different strategies, and GEO tracking should become an additional metric. This allows for diversifying traffic as a buffer against drops in Google.
Platform Diversification
TikTok SEO and SMO (Social Media Optimization) are becoming critical for consumer categories. LinkedIn remains the primary platform for B2B. YouTube is important for video content and educational materials. Participation in Reddit and other communities helps build thought leadership. The result is a reduction in dependence on Google from 80% to 40-50%.
Technical Optimization and Accessibility
Fixing Core Web Vitals must be mandatory: LCP less than 2.5 seconds, INP less than 200 milliseconds, CLS less than 0.1. A full audit for WCAG 2.2 compliance is an investment in the future. Studies show 37% traffic growth plus a 3-5% increase in conversion.
Quality Control of AI Content
You cannot simply let AI write content without supervision. The optimal model: AI creates a draft, a human edits and improves, an expert reviews the final result. A fact-checking system and a content update calendar (quarterly) ensure freshness. The result is ranking stability instead of drops of 40-80%.
Three Great Truths of 2025
The first great truth is that Google is no longer a search monopoly. 60% of Generation Z uses TikTok weekly to search for information. ChatGPT processes 2.5 billion prompts daily. Perplexity grows by 25% in four months. Result: SEO must be part of a larger strategy, not the entire strategy.
The second great truth: Position ranking is dead, citation lives. AI Overviews take 47% of clicks when present. Zero-click accounts for 60% of all searches and could reach 70% by the end of 2026. But AI citations bring 4.4 times more valuable traffic according to research. Result: We need to abandon “position number one” as a success metric.
The third great truth: Quality equals refined human expertise plus machine structure. Pure AI content loses due to lack of unique insights. Pure manual content loses due to slowness of production. AI as an assistant plus human editor plus expert reviewer create a winning combination. Result: A rethinking of the content creation workflow is necessary.
Predictions for 2026
May 2026 could bring the biggest Core Update of the year, expected after the December “momentum.” The EU investigation into parasite SEO will either conclude or expand. June 2026 will mark the full effect of WCAG 2.2 and BFSG after a 12-month transition period. Google is expected to strengthen accessibility as a ranking factor.
September 2026 may see the expansion of AI Overviews from 13% to 25-30% of queries. GEO will become a mandatory discipline, like SEO was in 2015. December 2026 could bring EU rulings regarding AI content and Google’s practices. ChatGPT’s market share could reach 2-3% versus the current 1%.
"SEO lives and dies by consistency."
John Mueller
The New Reality of Consistency
As John Mueller noted, SEO lives and dies with consistency. Constant updating and maintaining quality are more important than one-time optimizations. People are no longer looking for a set of blue links; they are looking for answers. Companies that understand this shift and adapt will not just survive, but thrive.
The era when one could manipulate algorithms through technical tricks is over. The new world of SEO demands genuine expertise, real experience, transparency, and constant dialogue with the audience across various channels. 2026 will be the time of “visibility everywhere,” where presence on Reddit, TikTok, and in ChatGPT answers will be just as important as traditional positions in Google.
Companies that invest in creating real value, building trust, and demonstrating real expertise will find their audience regardless of what algorithmic changes the future brings. This is not just a change in SEO; it is a fundamental transformation of how people search for and consume information in the digital age.


Frequently Asked Questions:
What is parasitic SEO and why does Google fight it?
Parasitic SEO is a practice where specialists pay authoritative publications (Forbes, Wall Street Journal, CNN) to place low-quality or sponsored content on their domains in order to leverage the high ranking of these sites. Google has actively penalized this practice since November 2024 under its Site Reputation Abuse policy.
Why is the zero-click rate increasing and how does it affect businesses?
58% of Google searches now end without a click to a website due to AI overviews, featured snippets, and other SERP features. This reduces direct traffic, but studies show that AI-referral traffic converts 23 times better and has 4.4 times higher value than traditional organic traffic.
What is E-E-A-T and why is it important in 2026?
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. In 2025, it shifted from being a recommendation to a mandatory requirement. Content must demonstrate the author’s real experience, backed by evidence, credentials, and transparent author information.
Can AI be used to create SEO content?
Yes, but only as an assistance tool, not for fully automated production. The optimal model: AI generates a draft, a human editor improves and adapts it, and an expert reviewer verifies factual accuracy. Pure AI content without human oversight has been actively penalized by Google since 2025.


