The state of search engine optimization in 2025 is characterized by an unprecedented confrontation between Google’s deep learning algorithms and sophisticated manipulation methods based on large language models. The Black Hat SEO ecosystem has transformed from primitive spam into an intelligent simulation of authority and user satisfaction. What used to provide 12 months of stable ranking now works for a maximum of 2-8 months before detection and sanctions.
Throughout 2025, Google released three major Core Updates (March, June, December) and a specialized August Spam Update, which radically changed the landscape of shadow promotion. The search engine’s main focus has shifted from analyzing individual pages to assessing holistic site signals through the QualityCopiaFireflySiteSignal module, which allows identifying scalable content abuse at the resource architecture level.
Danny Sullivan, Google Search Liaison, clearly outlined the system’s position: “Content created primarily for search engine rankings rather than to help people can perform poorly regardless of whether it was created by AI or a human.”
The key transformation lies in the fact that scalability is no longer a strategy. Anyone who copies 100,000 doorways with a single variable faces algorithmic death in a matter of days. Instead, the most effective black hat optimizers in 2025 focus on the quality of imitation and micro-scaling of 10 to 50 unique assets instead of thousands.
Evolution of Doorways and Mass Page Generation
The traditional understanding of doorways as static pages oversaturated with keywords has completely lost its relevance. In 2025, black hat optimizers shifted to creating dynamic content nodes using LLMs to generate texts that, at first glance, are indistinguishable from expert materials.
LLM-Generated Doorways: Practically Dead
Following the launch of the August 2025 Spam Update, Google systematically deindexed sites built on the principle of mass content generation. A typical scenario looked like this: a client launched 50,000 variations of the page "Best SEO Service in [City]," each with 90% content duplication. The result was the actual deindexing of the entire domain.
The technical reason is that Google uses NLP (Natural Language Processing) to detect repetitive linguistic patterns in AI content. The system recognizes identical sentence structures, predictable word distribution, and a lack of original depth of thought.
A real example: one client had eight million pages on disk, but Google indexed only 650,000 of them. After the penalty, even new high-quality articles stopped ranking because the domain was flagged by the SpamBrain system.
Programmatic SEO as Spam Camouflage
The line between legitimate programmatic SEO and spam in 2025 is defined by the concept of "added value." Google began mass deindexing projects where automation was used to clone content with minimal changes.
The main ban criterion is the lack of unique data or functionality (calculators, real reviews, proprietary databases) that would justify the existence of thousands of pages. Companies attempting to cover spam with Programmatic SEO technology faced Manual Actions after the March and June updates.
A typical penalty scenario: 200 pages of "Best Plumber in [City]" with identical content led to algorithmic punishment and Google's refusal to index new content.
Bordering on legality is "white hat programmatic SEO," where each page features real data from local sources, unique reviews from real clients, and different content architectures. This approach still works, but under intensified scrutiny.
The "Pie" Scheme in Traffic Arbitrage
In the context of traffic arbitrage, the term "Pie" (or Layer Cake) describes multi-layered user redirection structures. This scheme involves creating a "sandwich" of domains:
The Top Layer (Tier 1) consists of white, trusted sites or Parasite SEO pages on large platforms that gather organic traffic. These resources look legitimate to search engines.
The Middle Layer acts as a filter (cloaking) that cuts off Google bots via JavaScript fingerprinting and analysis of over 900 browser parameters. The system determines whether the visitor is a real person or a search robot.
The Bottom Layer is the target landing page with the offer, containing commercial content or violating Google policies.
Traffic "gluing" occurs through complex chains of 301 redirects and Canonical attribute manipulations, allowing link weight to pass from black hat doorways to the main project while minimizing the risk of direct sanctions. The efficiency in arbitrage is high, but the deindexing risk is rated as medium.
Link Manipulation: PBNs, Drops, and Injections
Links remain the currency of search promotion, but in 2025 Google finally shifted to assessing the contextual weight of a link, not just domain authority. This forced Private Blog Network owners to radically change their approach to hiding networks.
Hiding Traces in PBN Networks
In 2025, standard PBN hiding methods like different IP addresses and DNS became insufficient. Google uses advanced link graph analysis to detect closed networks through a system that considers shared infrastructure (DNS records, IP ranges, hosting provider patterns), AI-text patterns via deep NLP analysis to detect homogeneous authorship, link velocity (if 20 obscure sites suddenly link to one domain in three days), and anchor text distribution.
Black hat optimizers responded with a “fingerprint blurring” strategy. Instead of uniform WordPress sites, they began using different CMSs (Ghost, Hugo, static sites on S3). Link profiles are mixed: sites link not only to manipulative acceptors but also to large media outlets, Wikipedia, and government resources to simulate naturalness.
Fake author profiles with verified social signals (LinkedIn, X) are generated to pass E-E-A-T checks. Google learned to deindex such networks automatically if the system detects identical publication dynamics and the simultaneous appearance of links to a group of unrelated sites.
Real tactics for a successful PBN in 2025: 10-15 drops from different hosting providers (not budget ones), each site has a real author with different emails and IPs, links are given no more than 2-3 per month (low velocity), 40% of posts link to authoritative sites for a natural look. Result: often last 3-6 months before a soft penalty.
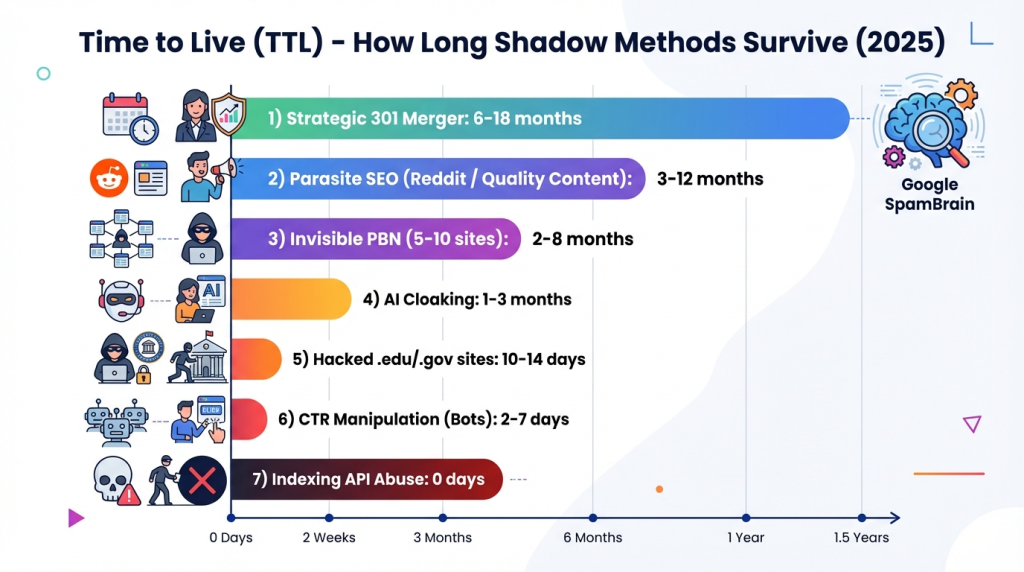
Classic PBNs in the style of 2014-2020 are deindexed in 30-90 days, as Google has a log database of known spam networks and compares new domains. Even “invisible” PBNs with maximum masking work for 2-8 months, after which Google’s meta-analysis detects the network.
Effectiveness of Expired Domains and 301 Redirects
The strategy of simply “gluing” authority via a 301 redirect from a drop domain effectively stopped working in 2025 when the topic changed. Google implemented a link weight reset mechanism (“Reset History”) if the site’s new content does not match its historical profile. This was officially enshrined in the “Expired Domain Abuse” policy in March 2024 and strengthened throughout 2025.
A 301 redirect still passes weight, but conditionally. If the drop is relevant to the new domain, the transfer is 70-90% of the old weight. If the drop had a spam history, Google resets the weight upon detecting a thematic change. If used for arbitrage, traffic redirection leads to a penalty.
The most effective method remains the “Strategic Merger,” where a successor page is created on the new domain that fully corresponds to the intent of the drop’s old popular page. In this case, Google can preserve up to 90% of link weight. The Time to Live of such strategies is 6-18 months with moderate risk, provided relevance is maintained and there is no spam history.
The “authority gluing” problem: old domains with 500+ links were often penalized for previous spam; Google assigns less weight if the region or language has changed; rare drops are subject to faster deindexing than before.
Relevance of Links from Hacked Sites
Using XSS injections and placing hidden links on hacked .edu and .gov sites moved into the ultra-high-risk category in 2025. Although such links still give a powerful short-term boost, their lifespan has shortened to 10-14 days.
In 2025, 135,000 compromised sites were detected. Links from .edu/.gov domains remain valuable but are detected within 24-48 hours. Time to Live for such links: 1-3 months before cleanup.
A typical attack example: a hacker compromises a WordPress plugin used on 50,000 sites, injects JavaScript to redirect to a casino, and 10,000 WordPress sites get infected in 72 hours. Google detects this, flags it as “malware” or “compromised,” and links are removed from the index in a week.
Expert conclusion: Link injection as a long-term ranking strategy is ineffective in 2025. Maximum effect is a one-time boost before detection. Old link exchanges (like “Sape”) are used mainly for promotion for low-frequency queries in geolocations with low competition, as their patterns have long been known to Google’s anti-spam team.
"The fact that third-party content can be high-quality does not negate the abuse of the main site's reputation to gain an unfair advantage."
Danny Sullivan
Parasite SEO and Site Reputation Abuse Policy
The year 2025 was a turning point for the Parasite SEO method. Following the announcement of the Site Reputation Abuse policy in May 2024, Google began actively applying Manual Actions against large publishers who allowed third parties to publish commercial content disguised as editorial material.

Definition and Google's Reaction
Site Reputation Abuse means publishing third-party material on a trusted domain to exploit its ranking signals. For example, thousands of SEO articles on Medium.com or affiliate content on Forbes masking as editorial reviews.
Danny Sullivan emphasizes: "Just because third-party content might be of high quality doesn't negate the fact that it's abusing the host site's reputation to gain an unfair advantage."
The method's status in 2025 is controversial. Algorithmic detection without manual sanctions was expected, but reality turned out differently: Google began issuing manual actions after the November 2024 update. The European Union even opened an investigation against Google regarding the unfair application of this policy, claiming that legitimate publishers are funded through guest content.

Platform Survival Analysis
Many authoritative domains lost positions:
Outlook India and Forbes were the main targets of the first wave of sanctions. Affiliate content sections were mass deindexed, especially materials on online casinos and dubious services.
Medium still works, but efficiency has dropped by 50-60% compared to previous years. Google is lowering trust in Medium as a spam host. Risk is moderate, as the platform still holds some authority.
Reddit works well, especially new subreddits. Risk is low, as it represents user-generated content that looks less automated. In 2025, these platforms became the main beneficiaries of updates, as Google prioritizes forums in SERPs, considering them a source of real human experience.
LinkedIn theoretically works but is under strict control. Branded content looks less spammy, but LinkedIn often removes spam materials. Risk is moderate.
Quora effectively no longer works due to mass SEO attacks in previous years. Google has reduced this platform's weight. Risk is high.
Forbes Guest Posts are still powerful if truly published through editorial review. Genuine editorial vetting ensures more trust; risk is low.

Real Parasite SEO Tactics in 2025
Publishing on Reddit with valuable content (not spam, real value), linking to your own page with context. Result: traffic, links, and social signals. Time to Live: 3-12 months until removed by moderators.
Medium with "natural" link retention: 1-2 links per article, not 10 to one domain. Result: sometimes ranks in 2-4 weeks. Risk is low if there is no mass publication.
LinkedIn Articles published within companies: publishing articles on behalf of multiple profiles. Result: ranks, but shorter duration than before. Risk is moderate.
This prompted black hat SEOs to mass-boost accounts and create fake discussion threads to take advantage of Google's trust in forums.
Behavioral Factor Cheating and CTR Manipulation
In 2025, behavioral factors became a dominant ranking signal in competitive niches. As Google increasingly relies on RankBrain and new satisfaction assessment systems, manipulating clicks and dwell time has become a mandatory element of Black Hat strategies.
Theory vs. Reality
Theoretically, Google uses CTR as a content quality signal: if a page has a higher-than-expected CTR, it is considered more relevant. However, Google has officially stated that CTR is too noisy a signal.
Internal documents leaked in the “Google Leak” of 2024 show a different picture: link velocity is the strongest signal in SpamBrain, anchor text pattern is second in impact, and CTR is only an auxiliary factor.
Lily Ray, an SEO expert, notes: “Content based on real experience is likely to become critical for standing out among the mass of AI-generated material.”
Use of AI Agents and Botnets
Instead of primitive click farms, autonomous AI agents are used in 2025. These bots do not just follow a link, but imitate complex behavior:
Branded search queries to strengthen entity authority. Bots type the company name into search to create an impression of brand popularity.
Page study: scrolling, text highlighting, clicking on inactive elements. This imitates the natural behavior of a user reading and interacting with content.
“Pogo-sticking” on competitor sites (quick return to SERP) and long stays on the target site (Dwell Time). This creates the impression that competitors do not satisfy the query, while the target site does.
Google detects CTR bots through analysis of click geography (are they all from one country), bounce rate (if visitors leave immediately), and time on page (if the bot is present for 2 seconds).
Effectiveness of CTR Manipulation in 2025
Different methods have varying effectiveness:
Microtask Workers (Fiverr, Upwork): Time to Live 2-7 days, position change by 2-3 spots, high risk due to low simulation quality.
Click bots with IP rotation: TTL 3-14 days, change by 1-5 positions, medium risk (detected by patterns).
Headless Browser (Puppeteer, Selenium): TTL 1-30 days, change by 1-3 positions, medium risk (behavior is imperfect).
Organic social sharing: TTL 1-3 months, change by 2-7 positions, low risk (real people).
Rand Fishkin’s experiment (2022-2024): organizing followers to search and click resulted in two weeks at the top, followed by a return to the original position. Conclusion: temporary boost without long-term effect.
CTR manipulation in 2025 gives a short 2-7 day boost, then the system returns the rank to its place. Effective only for Tier 2/3 projects before a capital sanction in a “Churn & Burn” format.
"Content based on real experience is likely to become critically important for standing out among the mass of AI-generated material."
Lily Ray
Technical Manipulations and Next-Gen Cloaking
Modern cloaking in 2025 is focused on bypassing AI detectors and Helpful Content assessment systems. Optimizers use content substitution technologies based on deep analysis of the incoming request.
AI-Powered Cloaking
Old methods (simple User-Agent filtering) are dead. New cloaking-as-a-service providers use JavaScript Fingerprinting (over 900 parameters: browser, fonts, GPU, timezone), Machine Learning Detection (system compares the user against 100,000 known bot-like behaviors), and Dynamic content swapping (one layout for Google, another for users). The cost of a basic version is around $100 per month.
Semantic Cloaking
search robots are served text perfectly optimized for LSI and Entities, while regular users see aggressive advertising or a simplified interface.
Interaction-based Content
the page loads empty for bots (if they don't execute JavaScript), and content appears only after real user interaction with the browser, complicating the work of automatic anti-spam scanners.
Effectiveness for SEO: showing "good" pages to Google and content violating policies to real users works for 1-3 months. Google launched runtime analysis to detect such tricks. Risk: Manual action for cloaking or complete deindexing.
Indexing API Abuse: Closed in September 2024
What it was before: illegitimate use of the Google Indexing API for mass indexing of any pages, which entered the index in minutes. Black hat optimizers could drive millions of pages into the index via multiple Google Cloud Platform service accounts.
What happened in September 2024: Google added a rigorous spam detection system for all API requests. The API no longer supports any content types, only job postings and live streams. Violations lead to immediate rejection and potential API access blocking.
Google implemented strict quotas (usually 200 URLs per day for new projects) and began requiring domain-level ownership verification for every request. Result: Churn & Burn schemes with Indexing API are absolutely ineffective in 2025.
"Content receives the lowest rating (Lowest) when text, images, or videos are copied, rephrased, AI-generated, or simply republished from another source without added value."
John Mueller
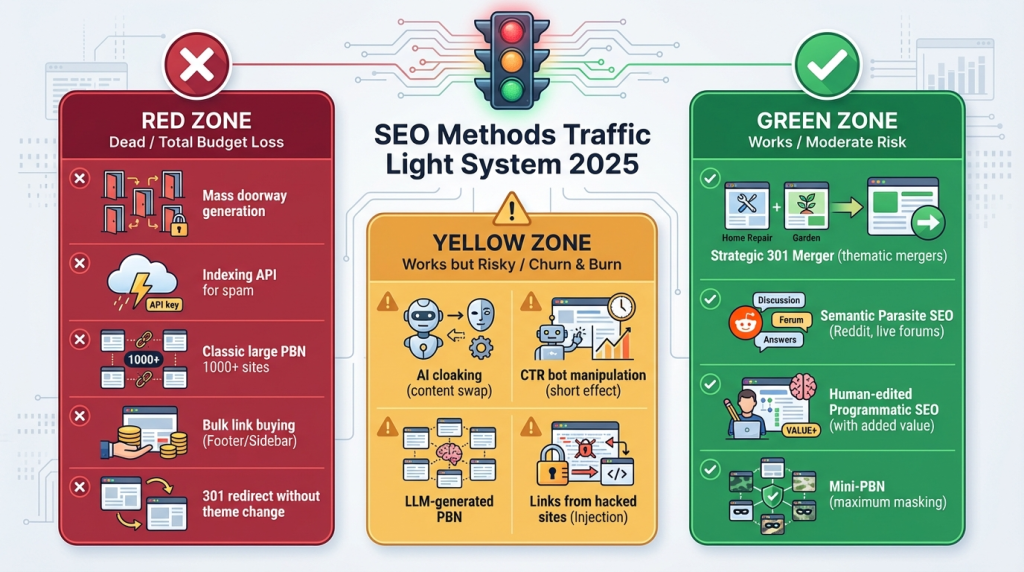
Classification of Methods by Efficiency and Risks
Still Working (High Efficiency with Moderate Costs)
Semantic Parasite SEO (Reddit/Quora): publishing quality content with natural links on authoritative platforms. TTL 3-12 months, ROI medium (2-5X), risk medium. Advice: quality content, few links.
Strategic 301 Merger: merging a relevant drop domain with a new project while maintaining thematic consistency. TTL 6-18 months, ROI medium (1-2X), risk moderate. Advice: relevance is mandatory, no spam history.
Human-edited Programmatic SEO: automatic generation with unique data, functionality, and human editing. TTL 3-18 months, ROI medium, risk low-medium. Advice: real value, adherence to E-E-A-T.
Miniature PBNs (5-10 drops): small networks with maximum footprint masking. TTL 2-8 months, ROI low-medium, risk medium-high. Advice: maximum footprint masking.
Working but Risky (Churn & Burn)
AI-driven CTR Manipulation: using bots for short-term position boosts. TTL 2-7 days, ROI very low, penalty probability 100% (but fast).
LLM-generated PBNs: networks with AI content and complex masking. TTL 1-3 months, ROI medium, risk 80-90%. A “fast burn” strategy with a high probability of manual sanctions.
Indexing API scaling: attempts to mass add pages via API (effectively closed). TTL practically zero after September 2024, efficiency zero.
Cloaking (AI-powered): content substitution for bots and users. TTL 1-3 months, ROI medium, risk 80-90%.
Content Scaling: mass generation without unique value. TTL 1-3 weeks, ROI low, penalty probability 95-100%.
Dead or Ineffective (Total Budget Loss)
Static Doorways: primitive pages with repetitive content. Detected by the system in hours via NLP structure analysis. Final year of death: 2025 (August update).
Mass LLM Generation: thousands of identical pages without editing. Cause of death: NLP and SpamBrain detection. Ineffective since 2025.
Classic PBNs (1000+ sites): large networks with obvious footprints. Detected in months, last live examples disappeared in 2023-2024.
Keyword Stuffing: oversaturation with keywords. Dead since Panda + NLP, death began in 2011.
Content Spinning: automatic paraphrasing. Reason: statistical detection, ineffective since 2013.
Link Buying (Obvious): buying links in footers and sidebars. Detected via anchor text analysis and velocity. Dead since 2012.
301 Redirect without Relevance: redirection from a drop of a different topic. Google resets weight upon detecting a context change.
IP Cloaking: primitive content substitution. Instant filtration by modern systems.
Google Sanctions and Recovery Time
Manual vs. Algorithmic Penalties
Manual Penalty
involves an explicit notification in Google Search Console, recovery time 10-30 days after submitting a reconsideration request. Frequency: over 400,000 per month. Response is operative after detection.
Algorithmic Penalty
has no notification (detected via traffic drop), recovery time 3-6 months (need to wait for the next core update). Frequency: millions of sites, majority of cases. Response is gradual via mass sanctions.
SpamBrain Real-Time Penalties (New in 2025)
The innovation of 2025 lies in the fact that Google started issuing algorithmically-triggered penalties in real-time, rather than waiting for core updates:
24 hours: a doorway site without unique content gets deindexed.
72 hours: a PBN detected as a network gets a soft penalty (ranking suppression).
One week: scaled content abuse leads to removal from SERP (complete deranking).
Reason for speed: SpamBrain machine learning models can issue decisions without waiting for scheduled updates. This radically shortened the Time to Live for most black hat methods.
Glenn Gabe, a well-known SEO auditor, warns: “Our AI-generated content ranks well—yes, that is exactly why Google will hit your site with manual actions for Scaled Content Abuse.”
Hybrid Security Strategy: How to Minimize Risks
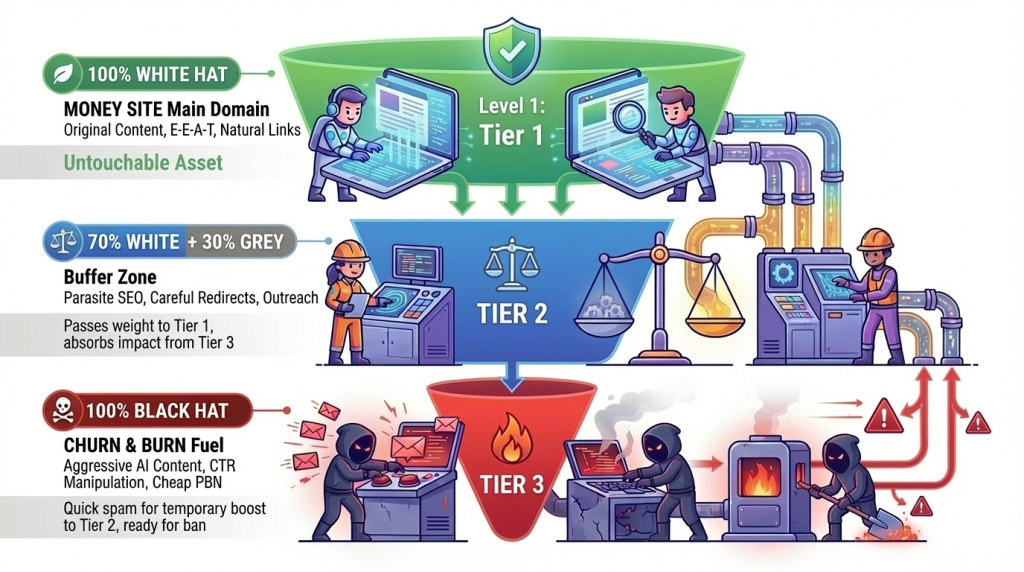
If risky techniques are used anyway, experts recommend a multi-level approach:
Tier 1 Project (main domain): 100% White Hat with original content, natural links, adherence to E-E-A-T. This level must be untouchable.
Tier 2 Projects (parallel, auxiliary domains): 70% White Hat + 30% Grey Hat with Parasite SEO, light expired domain redirects. These projects support the main one but do not expose it to direct risk.
Tier 3 Projects (“burnable” domains): 100% Black Hat in Churn & Burn format. All risky techniques are applied here before a capital sanction.
Security strategy: if Tier 3 burns, Tier 1 remains unharmed. This allows experimenting with aggressive methods without threatening the main asset.
Technical Recommendations
For PBNs, use VPS from different physical data centers, not a single provider. For Parasite SEO, one domain should contain a maximum of 1-2 links to a permanent target page. For AI content, minimum 60% AI-generated + 40% human editing. For links, vary anchor text (avoid exact matches), mix with brand mentions.
"AI-generated content is perfectly fine as long as it is curated by humans to ensure accuracy and originality."
Gary Illyes
Three Factors of Black Hat SEO Death in 2025
SpamBrain Evolution
machine learning that learns in real-time instead of waiting for core updates. The system analyzes billions of pages simultaneously and detects patterns instantly.
Real-Time Penalties
sanctions are issued in days, not months. The time between violation and punishment shortened from months to hours or days.
Cost-Benefit Collapse
six months of work on a PBN can cost $2-5k for a result that will be burned in two weeks. The economic viability of black hat methods has plummeted.
Black Hat SEO in 2025 is a game on a knife-edge with swift consequences. What used to provide 12 months of ranking now gives 2-8 months. While Time to Live shortens, costs and complexity grow exponentially.
For long-term ranking (over two years), White Hat with elements of cautious Grey Hat is the only viable strategy. For one-time earnings (affiliate campaigns), Tier 3 Churn & Burn relies on the quantity of projects instead of the quality of a single network.
Gary Illyes from Google summarizes the company’s philosophy: “AI content is perfectly fine if it undergoes human curation to ensure accuracy and originality.”
Understanding these mechanisms is critically important for cybersecurity specialists and white hat SEO engineers, as many methods considered black hat today subsequently transform into legitimate automation tools. However, in 2025, Google won the battle for scale, but is still losing the battle for context, which leaves narrow windows of opportunity for the most perceptive optimizers.


Frequently Asked Questions:
Do LLM-generated doorways work in 2025?
No, they are practically dead. Google uses NLP to detect repetitive linguistic patterns in AI-generated content. After the August 2025 Spam Update, sites relying on mass generation are deindexed within days. Domains receive a SpamBrain label, and even new high-quality articles stop ranking.
Which platforms for Parasite SEO still work?
Reddit performs well (low risk), Medium works but has declined by 50–60% (moderate risk), and LinkedIn is under strict control (moderate risk). Quora is largely ineffective (high risk). Forbes guest posts remain powerful when there is genuine editorial review (low risk).
What is the “Pies” scheme in affiliate marketing?
It is a multi-layered structure: Tier 1 (white, trusted sites that capture organic traffic), a middle layer (cloaking filters out Google bots), and a lower layer (the target page with the offer). These layers are connected through 301 redirects and canonical manipulation. Effectiveness is high in affiliate marketing, with moderate risk.
What is the safest strategy for long-term rankings?
A multi-tier approach: Tier 1 (100% White Hat, main domain), Tier 2 (70% White + 30% Grey Hat, supporting domains), and Tier 3 (100% Black Hat churn-and-burn projects). If Tier 3 burns out, Tier 1 remains unaffected.


